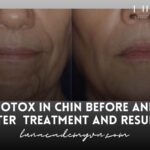
Botox, scientifically known as Botulinum toxin type A, is derived from the Clostridium botulinum bacteria. When used in controlled doses, Botox effectively reduces muscle movement in targeted areas by temporarily blocking nerve signals. This controlled paralysis minimizes wrinkles, giving the skin a smoother, younger appearance. Botox is primarily used for cosmetic purposes, particularly to soften lines on the forehead, around the eyes, and around the mouth. However, it also has therapeutic applications, such as reducing chronic migraines, alleviating excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), and managing muscle spasms.
The administration of Botox requires a highly controlled, professional approach. Since Botox is, by nature, a toxin, proper dosage and injection techniques are crucial for safe and effective results. As this treatment grows in popularity, however, questions naturally arise about its long-term effects on the body—particularly whether repeated Botox use could be harmful and, more specifically, whether Botox could cause cancer.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Cancer Risks: Does Botox Cause Cancer?
To answer does Botox cause cancer, it’s essential to understand what causes cancer. Cancer typically results from mutations in cellular DNA, causing cells to grow uncontrollably and form tumors. These mutations can be triggered by various factors, including lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, genetics, or contact with specific chemicals. Since Botox is a controlled toxin, it’s understandable that users would want to know if it has any carcinogenic (cancer-causing) properties.
Research on Botox and cancer has yet to establish a direct link between the two. Health authorities like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency continue to monitor and review Botox’s safety profile. Studies to date have shown no evidence that Botox injections cause cancer. This lack of connection between Botox and cancer means the treatment is generally considered safe for its intended cosmetic and medical purposes.
Is Botox Harmful Over Time?
When considering does Botox cause cancer, it’s also worth examining whether Botox could be harmful if used regularly over a long period. Botox’s effects typically last 3–6 months, leading many users to undergo repeat treatments to maintain their results. So, what happens if someone uses Botox for years or even decades?
Long-term studies on Botox indicate that the treatment is safe when administered by qualified professionals. Some mild side effects may accumulate over time, but they’re not linked to cancer. Potential long-term side effects include:
- Muscle Weakness and Atrophy: Repeatedly paralyzing facial muscles can lead to a slight weakening or reduction in muscle size, though this is typically reversible if Botox is discontinued.
- Skin Texture Changes: After many years of Botox treatments, some users notice slight changes in skin texture. This could be due to prolonged muscle relaxation or altered skin elasticity in treated areas.
- Decreased Effectiveness: Some individuals may develop antibodies to Botox, reducing its effectiveness. This isn’t harmful, but it could require higher doses or switching to different treatment types.
While these side effects don’t suggest that Botox is carcinogenic, understanding the potential for gradual changes with long-term use can help individuals make informed decisions about ongoing treatments.
What Are the Long-Term Side Effects of Botox?
When answering does Botox cause cancer, it’s also helpful to discuss Botox’s other long-term effects. Though cancer is not listed among known side effects, Botox has been associated with some minor long-term reactions.
Long-Term Effects of Botox
- Localized Muscle Weakness: With consistent use, Botox may cause localized muscle weakening in specific areas. This effect can be reduced by adjusting injection locations or frequency.
- Skin Thinning: Although rare, some patients report that areas repeatedly injected with Botox become slightly thinner over time.
- Resistance to Botox: Developing antibodies against Botox could make the treatment less effective over time.
While these side effects are minor and manageable, they show that Botox can have subtle effects over the long term. However, no evidence currently links Botox with any form of cancer, making it unlikely that Botox would have carcinogenic potential based on existing data.
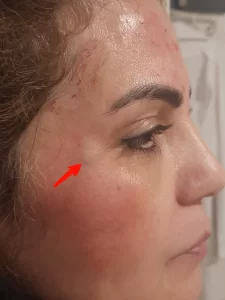
Botox Side Effects Pictures
For those researching does Botox cause cancer, visual documentation of Botox’s effects may offer insights. Botox’s most common side effects are typically temporary, including mild bruising, redness, and slight swelling at the injection site. Botox side effects pictures often show these minor effects, which usually resolve within days.
Some images also document more pronounced effects, such as slightly altered facial expressions, which can sometimes occur if Botox is overused or administered incorrectly. However, no images suggest any connection to cancer or visible tumors associated with Botox. These photos help set realistic expectations, helping patients understand what is typical and what is unlikely.
Does Botox Cause Cancer?
Now to address the core question directly: does Botox cause cancer? Based on available scientific evidence, Botox does not cause cancer. Botox’s mechanism is focused on muscle movement, targeting neuromuscular junctions to reduce movement in specific areas without affecting cell division or DNA, which are typically involved in cancer development.
To reassure those concerned, regulatory bodies like the FDA closely monitor Botox’s safety profile. Numerous studies confirm that Botox is safe for both short-term and long-term use when administered correctly. Importantly, Botox doesn’t introduce foreign materials into the body on a cellular level. The small doses used in treatments are temporary and eventually break down within the body, posing minimal risks to overall health.
The purified nature of Botox means it acts locally in the injection area without spreading significantly to other parts of the body. This limited impact makes it unlikely that Botox could have systemic effects capable of influencing cancer risk.
What to Expect After Undergoing Botox
For those considering Botox and wondering, does Botox cause cancer, it’s essential to understand what happens post-treatment. Most patients experience only mild side effects that last briefly, such as redness, bruising, or mild swelling. Generally, these resolve quickly, and most people can return to daily activities the same day.
While some individuals may worry about serious health impacts, Botox has been shown to be one of the safer cosmetic treatments when performed by certified professionals. No studies to date link Botox to cancer risk, and the treatment is extensively studied and monitored to ensure its safety for both cosmetic and therapeutic uses.
Conclusion: Does Botox Cause Cancer?
To summarize, the question does Botox cause cancer has been examined thoroughly in scientific research, and the answer is a clear “no.” Botox is safe when administered by qualified professionals, and current data does not suggest any link between Botox use and cancer development. The controlled and localized nature of Botox treatments minimizes systemic exposure, and there is no evidence of Botox causing DNA mutations or cellular changes that could lead to cancer.
While it’s always wise to consider potential long-term effects, those choosing Botox for cosmetic or medical purposes can feel reassured about its safety. Staying informed and consulting with trained professionals will allow Botox users to enjoy the benefits of this popular treatment with peace of mind.
Contact us via other platforms if you have any questions or requests that need to be answered quickly.
Tiktok: www.tiktok.com/@lunabeautyacademy6
Hotline: 034 254 0228
Email: lunabeautyacademy@gmail.com
Address: No. 29, Alley 140/1/2, Lane 140 Nguyen Xien, Thanh Xuan, Hanoi
Luna wishes you success and hopes you will have the best experiences at the academy. If you need advice or answers about anything, please leave your Contact Information With Us, the Luna team will contact you soon. Thank you for reading this article.