Can hyaluronic acid cause dry skin? This question is increasingly common in the realm of skincare, as consumers seek to understand the true effects of this popular ingredient. Hyaluronic acid has gained a stellar reputation as a hydrating powerhouse, yet there are instances where individuals report experiencing dryness or irritation after using products containing it. The paradox raises several questions about how and why hyaluronic acid might contribute to dryness, particularly when its primary function is to retain moisture. To navigate this conundrum, we must delve into the science behind hyaluronic acid, its role in skincare, and the various factors that can influence its effectiveness on the skin.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Hyaluronic Acid

Before we can appreciate whether or not hyaluronic acid contributes to dry skin, it is essential to understand what it is and how it functions within our bodies.
What is Hyaluronic Acid?
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring polysaccharide found throughout the human body, primarily in connective tissues, skin, and cartilage. Its unique ability to hold up to a thousand times its weight in water makes it an excellent candidate for hydration. It acts as a cushion and lubricant in the joints and eyes while also playing a significant role in retaining moisture in the skin.
What sets hyaluronic acid apart from other molecules is its remarkable capacity to attract and bind water, which is pivotal in maintaining skin elasticity and firmness. As we age or are exposed to environmental stressors, the natural levels of hyaluronic acid in our skin decline, leading to signs of aging such as wrinkles and loss of volume.
The Role of Hyaluronic Acid in the Skin
In the context of skincare, hyaluronic acid serves multiple purposes. It helps maintain skin hydration, provides structural support, and minimizes the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. When applied topically, hyaluronic acid penetrates the skin layers, drawing moisture from the environment and deeper skin layers into the epidermis.
The result is a plumped-up effect that leaves the skin looking fresh and youthful. However, the efficacy of hyaluronic acid can be influenced by external conditions, such as humidity levels, and individual skin types, which brings us back to the question at hand: can it cause dryness?
The Functionality of Hyaluronic Acid

Understanding the functionality of hyaluronic acid reveals insights into how it interacts with skin and its surrounding environment.
Moisture Retention Properties
The primary selling point of hyaluronic acid is its impressive moisture retention properties. When properly formulated, hyaluronic acid can create a moisture barrier on the skin’s surface, preventing transepidermal water loss (TEWL). This barrier effect is crucial for maintaining hydration levels, especially for those with dry or sensitive skin.
However, it’s important to recognize that the skin’s moisture balance is complex. In low-humidity environments, hyaluronic acid may draw moisture from the deeper skin layers instead of the air, potentially leading to a parched appearance. Hence, while it’s designed to hydrate, incorrect usage in unfavorable climates can ironically lead to increased dryness.
How Hyaluronic Acid Interacts with Skin Cells
When introduced into skincare routines, hyaluronic acid interacts with skin cells at multiple levels. On a cellular level, it enhances the production of collagen and elastin, fostering skin resilience and reducing the appearance of age-associated changes. Moreover, it aids in wound healing and inflammation reduction, making it a vital ingredient in formulations targeting acne-prone or sensitive skin types.
Despite these benefits, there can be nuances based on skin condition. Individuals with compromised skin barriers or underlying conditions may experience different interactions. Therefore, it is always prudent for users to evaluate their skin’s response to products containing hyaluronic acid.
Common Misconceptions About Hyaluronic Acid
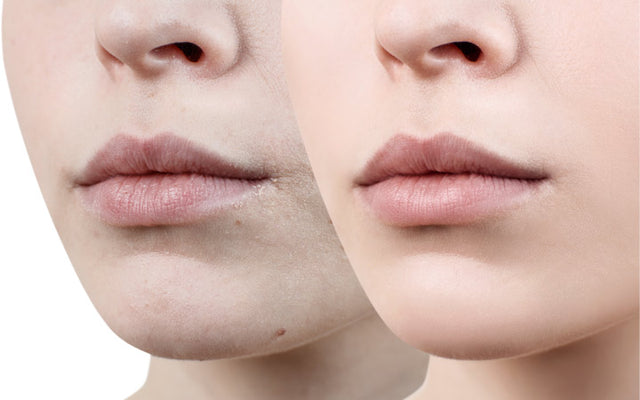

As with many popular skincare ingredients, there are numerous misconceptions surrounding hyaluronic acid, particularly concerning its hydration capabilities.
Myths Surrounding Hyaluronic Acid and Hydration
One prevalent myth suggests that hyaluronic acid alone is sufficient for complete hydration. While hyaluronic acid excels at drawing moisture, it does so most effectively when it is paired with an occlusive agent that prevents moisture from escaping. This misunderstanding can lead individuals to believe they’re adequately moisturizing their skin without considering the full spectrum of hydration needs.
Another misconception is that high concentrations of hyaluronic acid offer superior results. In reality, what matters more is the formulation and balance with other ingredients. A product with too much hyaluronic acid can become sticky or even lead to breakouts, depending on an individual’s skin type.
The Truth Behind Hyaluronic Acid Usage
The truth is that while hyaluronic acid is beneficial, it should not be seen as a standalone solution to skin concerns. Instead, it should be part of a broader skincare regimen that includes cleansing, exfoliating, and protecting the skin barrier. Users should also consider their lifestyle, dietary habits, and environmental factors affecting skin health.
Moreover, it’s essential to recognize that everyone’s skin is unique; what works for one person may not work for another. Personal experience, along with attentive observation of one’s skin, is key for understanding how hyaluronic acid affects individual hydration levels.
Potential Causes of Dry Skin
To fully comprehend whether hyaluronic acid can contribute to dryness, we must explore the various factors that can lead to skin dehydration.
Factors Contributing to Skin Dehydration
Dry skin can arise from numerous factors beyond just skincare products. Environmental conditions such as cold weather, wind, and low humidity can strip your skin of its moisture. Furthermore, lifestyle choices, including diet and hydration levels, play a crucial role in skin health.
Over-washing, using harsh soaps, or frequent exposure to hot water can compromise the skin’s barrier, leading to increased dryness. Certain medications, hormonal changes, and medical conditions like eczema or psoriasis can also contribute significantly to dehydrated skin.
Environmental Influences on Skin Health
The environment plays a vital role in skin hydration. For example, prolonged exposure to air conditioning or heating systems can dehydrate the skin. Similarly, pollution can hinder the skin’s ability to retain moisture by damaging the protective barrier.
Therefore, understanding your environment is critical. Those living in arid climates may find themselves battling dryness more than those in humid regions. This connection underscores the importance of tailoring skincare routines to address specific climate challenges and individual skin needs.
The Connection Between Hyaluronic Acid and Dry Skin

Now we can revisit the core question: how does hyaluronic acid relate to dry skin?
Can Hyaluronic Acid Lead to Dryness?
Under certain circumstances, hyaluronic acid can potentially lead to dryness rather than alleviating it. If used in a low-humidity environment, it may inadvertently pull moisture from the deeper layers of the skin rather than the atmosphere, thus causing dryness.
Additionally, improper use—such as applying it directly onto dry skin without a subsequent moisturizer—can exacerbate the situation. Without an occlusive layer to lock in moisture, the benefits of hyaluronic acid may not be fully realized, leading to the opposite of the intended effect.
Understanding Skin Types and Product Absorption
Different skin types absorb and react to hyaluronic acid uniquely. Oily skin may benefit from lightweight formulas that contain hyaluronic acid without feeling heavy, whereas dry or sensitive skin may require richer creams that incorporate occlusives for optimal hydration.
Individuals with compromised skin barriers may notice more pronounced effects like irritation or dryness, highlighting that selecting the right product for the specific skin type is imperative. Analyzing personal skin responses can guide users toward appropriate formulations that complement their individual needs.
How Hyaluronic Acid Works in Different Environments
The effectiveness of hyaluronic acid varies based on environmental conditions, which influences how it performs in different climates.
Performance in Humid Climates
In regions with high humidity, hyaluronic acid thrives. Under these conditions, it can effortlessly attract moisture from the air and effectively hydrate the skin. Users in humid areas often find that products containing hyaluronic acid leave their skin feeling soft and supple.
Here, hyaluronic acid can act almost like a magnet, drawing moisture into the skin and enhancing its overall appearance. This performance highlights the importance of environmental awareness when evaluating product efficacy.
Performance in Arid Climates
Conversely, in arid climates, the dynamics shift. Here, hyaluronic acid can draw moisture away from the skin itself, increasing dryness rather than alleviating it. For people living in such environments, it becomes crucial to pair hyaluronic acid treatments with rich moisturizers that can prevent moisture loss and protect the skin barrier.
Users in these climates may want to consider layering products, ensuring that they apply hyaluronic acid on damp skin and following it up with an occlusive moisturizer. Making adjustments according to local conditions can optimize the benefits of this powerful ingredient.
Signs of Dry Skin
Recognizing the signs of dry skin is critical to manage and address potential issues effectively.
Common Symptoms to Look For
Common symptoms of dry skin include tightness, flakiness, itching, redness, and a dull appearance. When skin feels consistently rough or lacks elasticity, it signals that hydration levels are not being maintained.
In some cases, dry skin may also lead to cracks and fissures, making the skin more susceptible to irritation and infection. It’s essential to stay vigilant for these signs, especially if incorporating new products into your skincare routine.
Differentiating Between Dry Skin and Dehydrated Skin
While often used interchangeably, dry skin and dehydrated skin have distinct meanings. Dry skin generally refers to a skin type characterized by a lack of oil, while dehydrated skin indicates a lack of water content.
Dehydrated skin can happen to anyone, regardless of skin type, and can manifest through symptoms like dullness and increased sensitivity. Understanding this difference is key to addressing skin concerns effectively, as it directs users toward appropriate treatments for either condition.
Proper Use of Hyaluronic Acid
Using hyaluronic acid correctly can enhance its potency while minimizing any adverse effects.
Best Practices for Application
To maximize the benefits of hyaluronic acid, apply it to slightly damp skin. This ensures that the ingredient can effectively draw moisture from both the environment and deeper layers of the skin. After application, follow up with a moisturizer that contains occlusive agents to seal in hydration.
Timing is also essential; using hyaluronic acid as part of your daily skincare routine can yield the best results, but be mindful of the environment—if the air is exceptionally dry, adjusting your routine may be necessary.
Tips for Combining with Other Ingredients
Combining hyaluronic acid with complementary ingredients can amplify its benefits. Pairing it with ceramides, glycerin, or squalane can provide added moisture and enhance skin barrier function. It’s advisable to avoid combining hyaluronic acid with strong acids or retinoids in the same step, as this could potentially lead to irritation.
Always patch-test new combinations to ensure compatibility with your skin’s unique needs.
Alternatives to Hyaluronic Acid
For those who experience adverse effects from hyaluronic acid, there are alternative ingredients that can also provide hydration.
Other Effective Moisturizing Agents
Ingredients such as glycerin, aloe vera, and shea butter serve as excellent alternatives. Glycerin, like hyaluronic acid, is a humectant that draws moisture into the skin, while aloe vera offers soothing properties alongside hydration. Shea butter provides an occlusive layer that locks in moisture, making it suitable for dry skin types.
Choosing the right combination of ingredients suited to your skin type can enable you to achieve the desired hydration without relying solely on hyaluronic acid.
Natural Remedies for Dry Skin
Many natural remedies can also help combat dry skin. Oils like coconut oil or argan oil are effective for sealing in moisture, while honey possesses natural humectant properties. Additionally, herbal infusions like chamomile or calendula can provide soothing relief for irritated skin.
Exploring holistic approaches can enrich your skincare journey, allowing for personalized solutions tailored to individual preferences and skin reactions.
Expert Opinions on Hyaluronic Acid and Dry Skin
Insights from professionals further illuminate the relationship between hyaluronic acid and skin hydration.
Dermatologists’ Insights
Dermatologists often emphasize the importance of proper formulation when it comes to defining the effects of hyaluronic acid. They recommend selecting high-quality products with balanced concentrations to suit individual skin needs.
Moreover, they advise against over-reliance on single products. Instead, they encourage users to cultivate a comprehensive skincare routine that addresses all aspects of skin health, including regular cleansing, exfoliation, and protection from environmental aggressors.
Skincare Specialists’ Recommendations
Skincare specialists highlight that the context of use is critical. They suggest formulating a routine that adapts to changing climates, skin conditions, and lifestyle factors. Regular consultations with skincare professionals can help tailor routines to individual needs and foster long-term skin health.
Ultimately, listening to your skin and being open to experiment can lead to discovering the perfect blend of ingredients that work harmoniously for you.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while hyaluronic acid is widely celebrated for its hydrating properties, it can indeed lead to dryness under specific circumstances. A thorough understanding of individual skin types, environmental factors, and proper application techniques can mitigate potential issues associated with its use. Awareness of the distinction between dry and dehydrated skin, along with incorporating complementary ingredients, will empower users to harness the full benefits of hyaluronic acid without falling victim to its pitfalls. Ultimately, skincare remains a deeply personal journey, and refining your routine through continuous learning and adaptation is the key to achieving radiant, hydrated skin.
Contact us via other platforms if you have any questions or requests that need to be answered quickly.
Tiktok: www.tiktok.com/@lunabeautyacademy6
Hotline: 034 254 0228
Email: lunabeautyacademy@gmail.com
Address: No. 29, Alley 140/1/2, Lane 140 Nguyen Xien, Thanh Xuan, Hanoi
Luna wishes you success and hopes you will have the best experiences at the academy. If you need advice or answers about anything, please leave your Contact Information With Us, the Luna team will contact you soon. Thank you for reading this article.