When it comes to the safe and effective use of aesthetic injectables such as Botox, understanding how long reconstituted Botox can be refrigerated is crucial for both medical professionals and patients. Reconstituted Botox refers to the process of mixing powdered botulinum toxin with a sterile solution to create an injectable form. The stability and efficacy of this product are largely dependent on proper storage techniques, particularly temperature control. In this article, we will delve deep into the topic of reconstituted Botox, exploring its composition, storing methods, potential risks associated with improper storage, and best practices to ensure its effectiveness when administered.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Reconstituted Botox and Its Composition
To understand the importance of refrigeration for reconstituted Botox, one must first grasp its fundamental characteristics, including what reconstituted Botox actually is, the role of botulinum toxin in aesthetic procedures, and what contributes to its stability.
What is Reconstituted Botox?
Reconstituted Botox is essentially the injectable version of botulinum toxin type A, which is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Initially, the toxin is stored in a dry state, typically in vials that can last for an extended period without losing potency. However, once the powdered form of Botox has been mixed with a diluent—usually saline—it becomes a liquid ready for injection. This process is known as reconstitution.
The ability to reconstitute Botox allows practitioners to customize the dosage and concentration required for individual patients, tailoring treatments to their specific needs. However, while reconstitution opens up possibilities for personalized aesthetic treatments, it also introduces challenges concerning storage and shelf life. As soon as Botox is reconstituted, it becomes susceptible to various environmental factors that could compromise its integrity and effectiveness, making it imperative to establish a well-defined storage protocol.
The Role of Botulinum Toxin in Aesthetic Procedures
Botulinum toxin has revolutionized the field of aesthetics since it was first approved for cosmetic use. Administered through injections, Botox temporarily paralyzes muscles by blocking nerve signals, resulting in a reduction of muscular contractions that lead to wrinkle formation. It is widely used in areas such as the forehead, crow’s feet, and frown lines, offering individuals a youthful appearance without the need for invasive surgical procedures.
While the aesthetic benefits of Botox are well-documented, it is essential to acknowledge that the safety and effectiveness of these treatments hinge on the proper handling and storage of the product. A compromised batch of reconstituted Botox can not only fail to deliver the desired results but may also pose health risks to patients.
Composition and Stability of Reconstituted Botox
The composition of reconstituted Botox includes the active ingredient (botulinum toxin) and a diluent such as sterile saline or bacteriostatic water. This mixture creates a solution that is easy to inject; however, it is important to note that the stability of reconstituted Botox is affected by multiple factors including temperature, light exposure, and time.
Studies suggest that reconstituted Botox can begin to degrade shortly after preparation if not stored correctly. Even slight deviations in storage conditions can impact the efficacy of the toxin, making it vital to adhere strictly to recommended guidelines. Therefore, understanding the chemical makeup and stability of reconstituted Botox provides insight into why proper refrigeration practices are so critical.
Importance of Proper Storage for Reconstituted Botox

Proper storage is fundamental to maintaining the efficacy of reconstituted Botox. Without appropriate temperature management, the risk of degradation increases, potentially leading to ineffective treatment outcomes. Here, we explore why temperature control is so crucial and the potential consequences of neglecting proper storage protocols.
Why Temperature Management is Critical
Temperature plays a pivotal role in the preservation of biological products like reconstituted Botox. The ideal storage conditions involve refrigeration, generally at temperatures between 2°C and 8°C. Storing Botox outside of this temperature range can accelerate its breakdown, rendering it ineffective for treatment.
When exposed to higher temperatures, the proteins within the Botox solution may undergo denaturation—a process where the protein structure is altered, causing loss of function. Similarly, extreme cold can also negatively affect the solution. Thus, maintaining a stable and controlled temperature is essential to extend the shelf life and ensure the product’s effectiveness.
Potential Risks of Improper Storage
Improper storage of reconstituted Botox can lead to several risks. Firstly, there is the risk of therapeutic failure. Patients receiving injections from improperly stored Botox may find that the treatment does not work as expected, leading to dissatisfaction and potential financial losses for both the patient and practitioner.
Moreover, there are serious safety concerns associated with using degraded Botox. While rare, administering ineffective or altered Botox could result in unexpected side effects or complications, which could harm the patient’s health and tarnish the practitioner’s reputation.
Furthermore, from a legal standpoint, practitioners who do not adhere to proper storage guidelines might face liability issues should any adverse events occur as a result of improper handling. Therefore, understanding the risks involved underscores the necessity for stringent storage protocols.
Recommended Storage Conditions for Reconstituted Botox
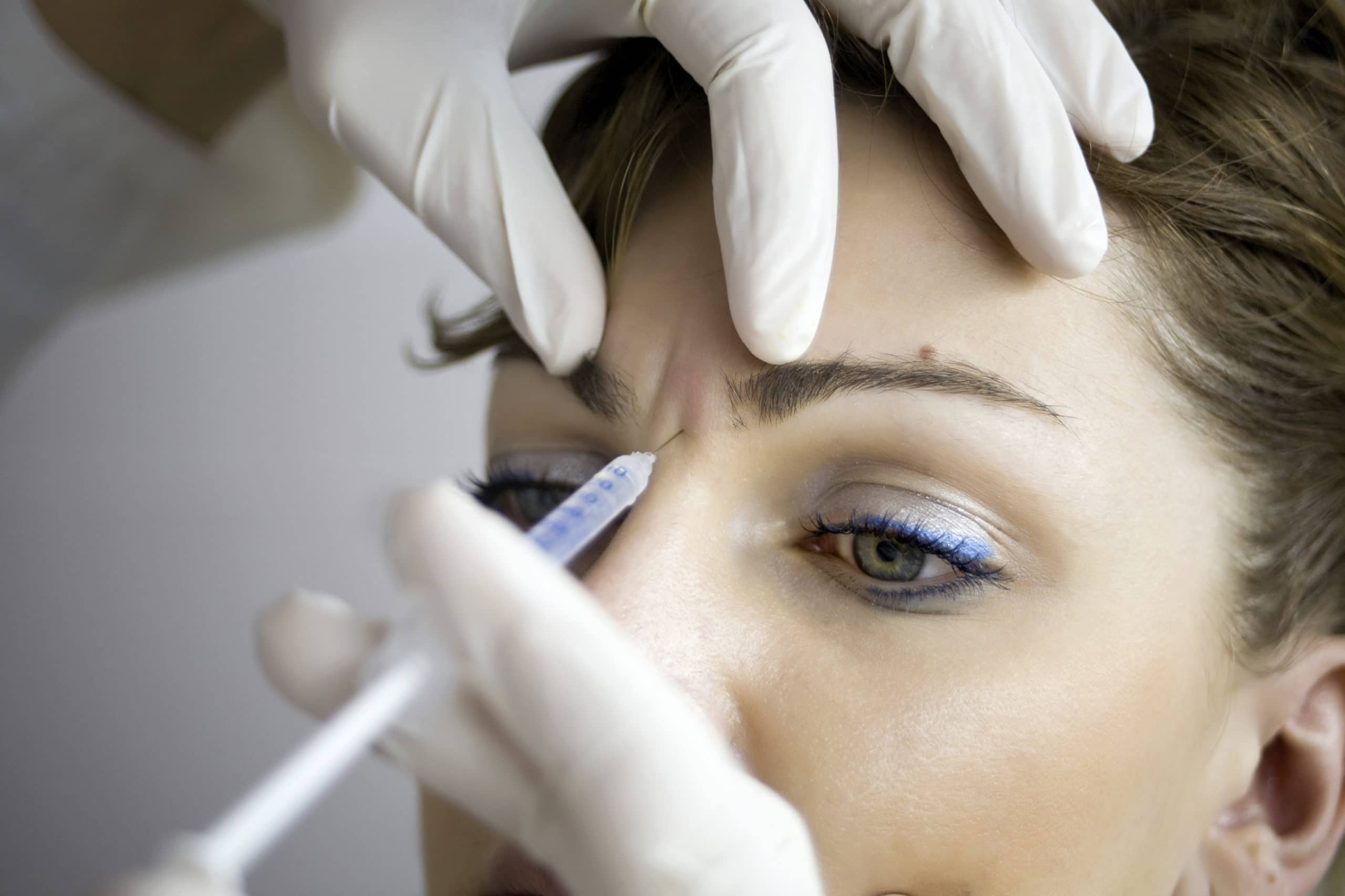
To maximize the effectiveness of reconstituted Botox, adhering to specific storage conditions is paramount. This section outlines the ideal refrigeration temperatures, duration guidelines, and signs of degradation to monitor for successful preservation.
Ideal Refrigeration Temperatures
The optimal temperature for storing reconstituted Botox is between 2°C and 8°C. This range prevents the breakdown of the active ingredients while maintaining the overall integrity of the solution.
It’s worth noting that although refrigeration is necessary, practitioners should avoid storing Botox in the freezer. Freezing can cause irreversible damage to the structure of the botulinum toxin, leading to reduced effectiveness and undesirable outcomes when injected. Moreover, fluctuations in temperature should also be avoided; thus, placing Botox in the door of the refrigerator—where the temperature tends to fluctuate more—is discouraged.
Storage Duration Guidelines
Once reconstituted, Botox has storage limitations that practitioners must respect. Generally, reconstituted Botox can be refrigerated for up to 24 hours before its effectiveness begins to decline. Although some sources may suggest that it can be stored for longer periods, it’s always best to err on the side of caution.
In practice, having a policy of using reconstituted Botox within 24 hours ensures that you provide your patients with the most effective treatment possible. While it may seem convenient to prepare larger batches for future use, the risks of degradation outweigh the benefits of convenience.
Signs of Degradation in Botox
Identifying signs of degradation is critical to ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy. Some common indicators that reconstituted Botox may have degraded include changes in color, clarity, or consistency of the solution.
A properly prepared Botox solution should be clear and free of particles. If the solution appears cloudy, discolored, or contains visible particles, it should not be used and must be disposed of immediately. Additionally, any unusual odor emanating from the vial could signal microbial contamination, warranting disposal.
Practitioners should routinely inspect their stored Botox prior to use to ensure that it meets quality standards, further reinforcing the importance of proper storage protocols.
Factors Influencing the Shelf Life of Reconstituted Botox

The shelf life of reconstituted Botox is influenced by several factors beyond just temperature. Key elements such as the quality of water used for reconstitution, handling techniques before refrigeration, and adherence to manufacturer recommendations play critical roles in determining how long the product remains effective.
Quality of Water Used for Reconstitution
The choice of diluent plays an essential role in the stability of reconstituted Botox. Sterile saline is the preferred diluent because it minimizes the risk of contamination and ensures that the solution maintains its sterility and effectiveness for a longer period.
Using non-sterile water or other solutions can introduce harmful bacteria into the mixture, increasing the likelihood of degradation and infection post-injection. Therefore, employing high-quality, sterile diluents during the reconstitution process significantly helps to preserve the integrity of the botulinum toxin.
Handling Techniques Before Refrigeration
The way practitioners handle Botox during the reconstitution process can also affect its shelf life. For instance, introducing contaminants through unwashed hands or non-sterile instruments can compromise the solution’s quality.
Practictioners should always maintain a sterile environment during preparation and avoid touching the tip of the needle or the syringe plunger to minimize the risk of contamination. Following strict aseptic techniques not only ensures the safety of the product but also safeguards patient health.
Manufacturer Recommendations
Manufacturers often provide specific guidelines regarding the reconstitution and storage of their products. These recommendations are based on extensive research and testing to determine the optimal conditions for maintaining the integrity of the substance.
It is crucial for practitioners to familiarize themselves with these guidelines and adhere to them diligently. Ignoring manufacturer recommendations could lead to compromised treatments and could ultimately impact patient outcomes negatively.
Best Practices for Storing Reconstituted Botox
Implementing best practices for storing reconstituted Botox is essential for preserving its efficacy and ensuring patient safety. This section discusses the importance of using appropriate storage containers, maintaining a stable refrigerator environment, and keeping accurate records for reference.
Using an Appropriate Storage Container
Selecting the right storage container for reconstituted Botox is vital. Practitioners should utilize the original vial in which the Botox was supplied, as it is designed to hold the solution securely and prevent contamination.
Transferring Botox into different containers not only increases the risk of contamination but can also expose the solution to environmental factors that might compromise its effectiveness. Always ensure that the vial is tightly sealed before placing it in the refrigerator to maintain the appropriate storage conditions.
Maintaining a Stable Refrigerator Environment
The refrigerator environment should be monitored regularly to ensure that it maintains the appropriate temperature range for storing reconstituted Botox. Investing in a reliable thermometer to measure internal temperatures can help identify fluctuations and enable corrective actions quickly.
Minimizing the frequency of opening the refrigerator door and avoiding overcrowding inside are additional strategies to maintain a stable environment. Regular maintenance and calibration of the refrigerator will also ensure optimal performance and prolong the shelf life of stored products.
Labeling and Dating Bottles for Reference
Keeping track of when Botox is reconstituted is crucial for establishing timelines for usage. Labeling each vial with the date and time of reconstitution serves as a quick reference for practitioners and ensures compliance with storage duration guidelines.
Having a structured labeling system helps eliminate confusion and enables practitioners to track the age of the product easily. This simple yet effective practice fosters accountability and enhances patient safety by ensuring that only high-quality Botox is utilized for treatments.
Common Misconceptions About Reconstituted Botox
Despite the extensive information available about Botox, many misconceptions persist. Addressing these myths is important for promoting safe practices and informed decision-making among both practitioners and patients.
Myths About Freezing Botox
One prevalent misconception exists surrounding the freezing of Botox. Some individuals believe that storing Botox in the freezer is a practical method for extending its shelf life. However, this is far from the truth.
Freezing can cause irreversible damage to the delicate protein structure of botulinum toxin. Once thawed, the effectiveness of the product diminishes significantly, leading to suboptimal treatment outcomes. It is essential to dispel this myth to promote safer storage practices and protect patient welfare.
Misunderstandings Regarding Expiration Dates
Another common misunderstanding revolves around expiration dates on Botox vials. Many assume that as long as the vial is unopened, it remains usable past the indicated expiration date.
While unopened vials do have a longer shelf life, once Botox is reconstituted, the clock starts ticking. Adhering to storage timeframes is imperative, as the reconstituted product must be used within a limited period to ensure efficacy. Educating patients and practitioners on the significance of these expiration guidelines is essential to maintaining the highest safety standards.
Handling Wasted or Leftover Botox
Handling leftover or wasted Botox requires careful consideration to ensure compliance with safety regulations and ethical practice. Discussing protocols for disposing of unused Botox and understanding the impact of time on efficacy once bottled is crucial in this area.
Protocols for Disposing of Unused Botox
Unused Botox must be disposed of according to specific regulations and guidelines to minimize environmental impact and safeguard public health. Healthcare facilities are typically required to follow established waste management protocols for hazardous substances.
Practitioners must take care to dispose of any leftover or expired Botox in designated biohazard containers specifically designed for sharps and pharmaceutical waste. By following proper disposal protocols, practitioners not only comply with regulations but also contribute to community safety.
Impact of Time on Efficacy Once Bottled
Once reconstituted, the efficacy of Botox diminishes over time. While it may still appear visually intact, the biochemical activity of the neurotoxin declines, leading to potentially less effective results upon administration.
Therefore, it is essential for practitioners to avoid reliance on leftover Botox from previous reconstitutions. Each time a vial is opened and reconstituted, a new timeline begins, and using the product beyond its recommended period significantly increases the risk of subpar treatment outcomes.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
The handling of Botox is governed by various legal and regulatory frameworks aimed at preserving public health and safety. Understanding these guidelines is integral for healthcare practitioners working with this potent substance.
FDA Guidelines on Botox Storage
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provides comprehensive guidelines for the storage and handling of Botox and other injectables. These guidelines emphasize the importance of temperature control, sterility, and proper reconstitution techniques to ensure patient safety.
Healthcare providers must keep abreast of these guidelines and apply them consistently in their practice. Non-compliance could result in legal ramifications and jeopardize patient health, making it essential to remain informed and proactive in adhering to FDA recommendations.
Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
In addition to FDA guidelines, practitioners must comply with other local and state healthcare regulations governing the use and storage of injectable products. These regulations are designed to protect patients and uphold the integrity of healthcare practices.
Regular training sessions and continuing education programs can help practitioners stay updated on legal obligations and best practices for handling Botox responsibly. Engaging with professional organizations and resources can enhance knowledge and reinforce commitment to patient safety.
Conclusion
Understanding how long reconstituted Botox can be refrigerated is fundamental to ensuring that this powerful treatment remains safe and effective for patients. By recognizing the complexities of reconstituted Botox, the importance of proper storage, and the best practices for handling this product, practitioners can maximize the efficacy of their treatments while safeguarding patient health.
As the field of aesthetics continues to evolve, ongoing education and adherence to established guidelines will be paramount for delivering exceptional patient care and achieving optimal outcomes. Whether you are a practitioner or a patient considering Botox treatments, being informed and diligent about storage practices can make all the difference in ensuring a positive experience.
Contact us via other platforms if you have any questions or requests that need to be answered quickly.
Tiktok: www.tiktok.com/@lunabeautyacademy6
Hotline: 034 254 0228
Email: lunabeautyacademy@gmail.com
Address: No. 29, Alley 140/1/2, Lane 140 Nguyen Xien, Thanh Xuan, Hanoi
Luna wishes you success and hopes you will have the best experiences at the academy. If you need advice or answers about anything, please leave your Contact Information With Us, the Luna team will contact you soon. Thank you for reading this article.